At the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, the US military launched a secret campaign to discredit China’s Sinovac inoculation and to counter what it perceived as China’s growing influence in the Philippines, according to a new Reuters investigation.
According to a new Reuters investigation, the clandestine operation hit the Philippines which had been hit particularly hard by the virus. I should know. I was in Metro Manila at the time.
In 2020, I released two reports on the pandemic and its international human and economic costs. The situation was particularly dire in the Philippines. I took the Sinovac shot twice and talked with some who were afraid to do so and chose to wait. Since then, I have wondered what happened to them.
US troll farms against Chinese Sinovac
The covert US military operation was particularly harmful because, as Reuters put it, “it aimed to sow doubt about the safety and efficacy of vaccines and other life-saving aid that was being supplied by China.”
How did it happen? Fake internet accounts impersonating Filipinos and used by US military’s propaganda were transformed into an anti-vax campaign. As Filipino public health officials struggled to contain the epidemic, the covert operation morphed social media posts into troll farms decrying the quality of face masks, test kits and especially the first vaccine that would become available in the Philippines – China’s Sinovac inoculation.
Reuters identified 300 accounts on X (Twitter) matching descriptions shared by former US military officials familiar with the Philippines operation. They urged Filipinos “not to trust the China vax, which was a “rat killer” and so on.
The origins of the US operation went back to the pre-pandemic 2019, when Trump’s defense secretary Mark Esper signed a secret order paving the way to the launch of the campaign. As Pentagon’s “competition” with China was identified with “active combat,” it enabled the military to bypass the State Department in its psychological warfare (psyop) operations. Ironically, that year, Esper was shaking hands in the Philippines with his counterpart Delfin Lorenzana; a meeting that was later linked with pledges of quick vax delivery and military cooperation, as reflected by a Rappler report.
From PH and Southeast Asia to Central Asia and the Middle East
Pentagon’s active use of social media tools began around 2010, with the onset of the Obama pivot to Asia, “leveraging phony accounts to spread messages of sympathetic local voices – themselves often secretly paid by the United States government.” Today, the US military employs an extensive ecosystem of social media influencers, fronts and covertly-placed digital ads to influence overseas audiences. In the Philippines, these ops are fostering an atmosphere of fear and political paranoia.
Most social media accounts were created in the summer of 2020 and centered on the slogan #Chinaangvirus. The anti-vax effort started in spring of 2020 expanding beyond Southeast Asia before it was terminated in mid-2021. Some of the set of fake social media accounts used by the US military “were active for more than five years,” according to Reuters.
After the successful test-run in the Philippines and Southeast Asia, the clandestine propaganda campaign was tailored to and recycled among local audiences across Central Asia and the Middle East. It was designed to spread fear of China’s vaccines among Muslims when the virus was killing tens of thousands of people daily.
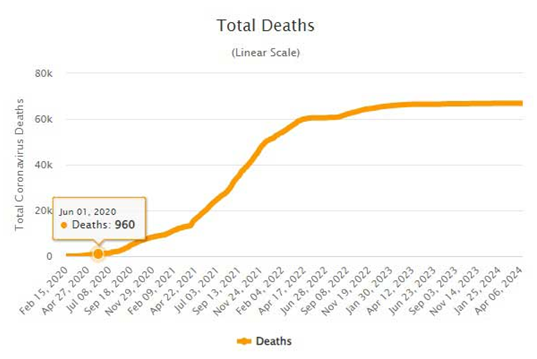
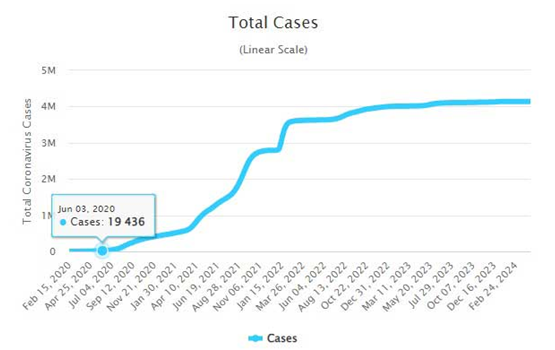
But why was the timing so destructive in the Philippines? Two (linear-scale) charts tell the story. When the US military anti-vax operation kicked in, there were fewer than 20,000 detected cases in the country. In the next three months, that figure surged to 215,000 and by the end of the year it exceeded 460,000, soaring to 2.8 million by the year-end of 2021. In mid-2021, the Philippines still had one of the worst inoculation rates in Southeast Asia. The difficulty in vaccinating the population, thanks in part to the covert US military op, contributed to the worst death rate in the region.